Email id.
-
-
Location
Get Direction
-
Phone No.
+91 9892466429
Email id.
Location
Phone No.

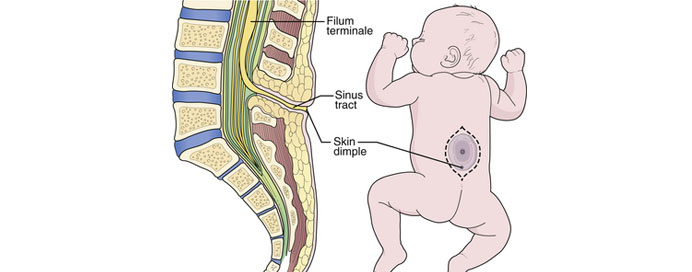
Spinal Dysraphism refers to a group of congenital spinal abnormalities, such as spina bifida, tethered cord, and lipomeningocele, where the spine and spinal cord do not form properly during development. Surgery is performed to protect the spinal cord, prevent neurological deterioration, and improve mobility, bladder function, and overall quality of life. Early surgical intervention is crucial to avoid long-term complications and to support healthier growth and development in children.